1) Initializing variable when you declare
declare @val as int =0
declare @currentdate as datetime = getdate()
print @val
print @currentdate
2) Compound assignment operators
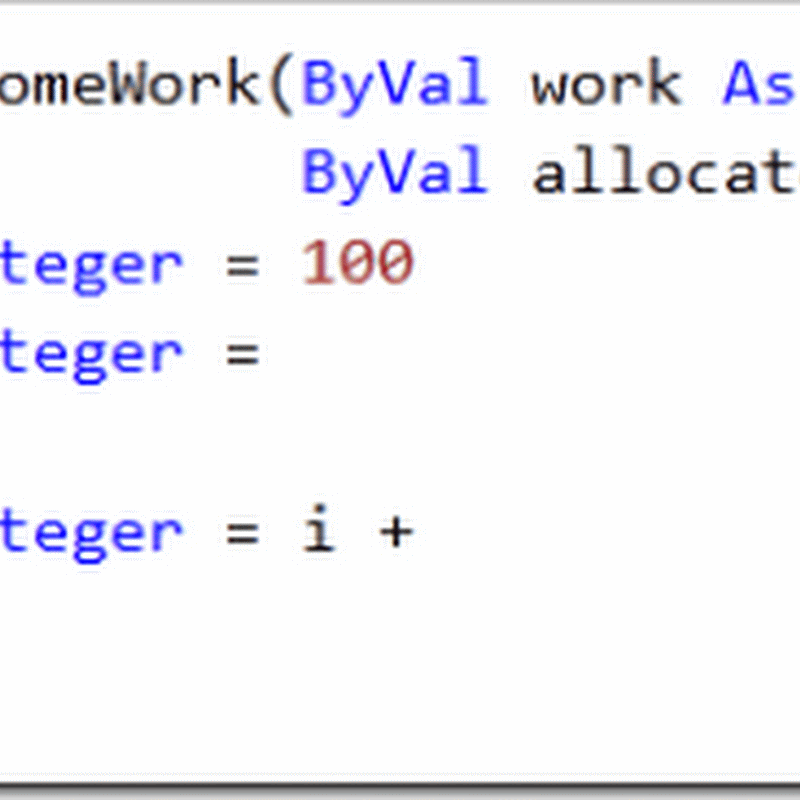
–operator like +=,-=,/=,*/,%=
declare @val as int = 0
set @val += 10;
print @val
3) Add multiple row in single Insert Statement
CREATE TABLE Employee
(
EmpId int,
EmpCode varchar(50),
EmpName varchar(50)
);
INSERT INTO Employee(EmpId, EmpCode,EmpName)
VALUES
(1, 'emp1','emp1'),
(2, 'emp1','emp1'),
(3, 'emp1','emp1');
select * from Employee
4) New Data Types | Data Type | Data Type Use |
| Date | The Date property returns a Date data type. |
| Time | Returns values for any valid time of day between 00:00:00 and 23:59:59:9999999. It has a length of at least 8 positions and contains the time in hours,minutes, seconds and fractional seconds. |
| DateTime2 | DateTime2 is an extension of the existing DATETIME type. It has a large date range and large default fractional precision. It has a length of at least 19 positions. |
| DateTimeOffSet | Returns values for year, month, day, valid time of day between 00:00:00 and 23:59:59:9999999 and offset, in hours, from UTC. It has a length of at least 25 positions. |
| Hierarchyid | The HierarchyId property is used to identify a position in a hierarchy. |
| Geography | The SQL Server geography data type stores ellipsoidal (round-earth) data, such as GPS latitude and longitude coordinates |
| Geometry | The Geometry property contains spatial data that represents information about the physical location and shape of geometric objects. |
HierarchyId Data Type 1: --Create Table Employee 2: CREATE TABLE Employee 3: ( 4: EmpId int, 5: EmpBossId HIERARCHYID, 6: --GetLevel --> returns the level of the current node in the hierarchy 7: EmpLevel as EmpBossId.GetLevel() PERSISTED, 8: EmpCode varchar(50), 9: EmpName varchar(50) 10: ); 11: Go 12: -- Create Insert Store Procedure 13: Alter PROCEDURE Employee_isp 14: @empid int, 15: @empbossid int, 16: @empcode varchar(50), 17: @empname varchar(50) 18: AS 19: BEGIN 20: declare @hid HIERARCHYID,@empboss_hid HIERARCHYID,@last_hid HIERARCHYID 21: 22: if @empbossid = 0 23: begin 24: set @hid = HIERARCHYID::GetRoot(); 25: end 26: else 27: begin 28: 29: SET @empboss_hid = (SELECT EmpBossId FROM Employee WHERE empid = @empbossid); 30: SET @last_hid = (SELECT MAX(EmpBossId) FROM Employee WHERE EmpBossId.GetAncestor(1)= @empboss_hid); 31: SET @hid = @empboss_hid.GetDescendant(@last_hid, NULL); 32: end 33: INSERT INTO Employee(empid, EmpBossId, EmpCode, EmpName) 34: VALUES(@empid, @hid, @empcode, @empname); 35: END 36: GO 37: --insert data 38: -- A1 39: -- AL1 AR1 40: -- AL1L AL1R AR1L AR1R 41: -- 42: -- 43: EXEC Employee_isp @empid = 1, @empbossid = 0, @empcode = 'A1' ,@empname = 'A1'; 44: EXEC Employee_isp @empid = 2, @empbossid = 1, @empcode = 'AL1' ,@empname = 'AL1'; 45: EXEC Employee_isp @empid = 3, @empbossid = 1, @empcode = 'AR1' ,@empname = 'AR1'; 46: EXEC Employee_isp @empid = 4, @empbossid = 2, @empcode = 'AL1L' ,@empname = 'AL1L'; 47: EXEC Employee_isp @empid = 5, @empbossid = 2, @empcode = 'AL1R' ,@empname = 'AL1R'; 48: EXEC Employee_isp @empid = 6, @empbossid = 3, @empcode = 'AR1L' ,@empname = 'AR1L'; 49: EXEC Employee_isp @empid = 7, @empbossid = 3, @empcode = 'AR1R' ,@empname = 'AR1R';Inserted Data Into Table Different Selection Criteria :1) Find Employee As Per their Level means Grade select * from Employee where Emplevel = 22) Get Child Node SELECT Child.empid, Child.empname FROM Employee AS Parent JOIN Employee AS Child
ON Parent.empid = 2 AND child.empbossid.IsDescendantOf(Parent.empbossid) = 1;3) Get Parent NodeSELECT parent.empid, parent.empname
FROM Employee AS Parent JOIN Employee AS Child
ON child.empid = 4 AND child.empbossid.IsDescendantOf(Parent.empbossid) = 1;more on HierarchyId Data Types refer:http://amitpatriwala.wordpress.com/2009/10/23/hierarchyid-data-type/5) Introduced New Functions| Function Name | Function Use |
| SYSDATETIME | Returns current date and time as DateTime2 value. |
| SYSUTCDATETIME | Returns current date and time in UTC as DateTime2 value |
| SYSDATETIMEOFFSET | Returns current date and time along with the system time zone as a DATETIMEOFFSET value |
| SWITCHOFFSET | Adjusts an input DATETIMEOFFSET value to a specified time zone, while preserving the UTC value. For example, the following code adjusts the current system datetimeoffset value to time zone GMT +05:00: SELECT SWITCHOFFSET(SYSDATETIMEOFFSET(), ‘-05:00′); |
| TODATETIMEOFFSET | sets the time zone offset of an input date and time value |
6) Support Large User Define Types [UDT]Sql Server 2008 supports large UDT,large UDTs can now reach up to 2 GB in size. Reference Sites: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc721270.aspx
0 Please Share a Your Opinion.: